

 Materials
Materials Materials. A
right mouse click on Materials
opens a drop-down menu where the user is able to call the Edit
dialog box. It shows a list of all available materials.
The icons on the top of the dialog box enable the following actions:
Materials. A
right mouse click on Materials
opens a drop-down menu where the user is able to call the Edit
dialog box. It shows a list of all available materials.
The icons on the top of the dialog box enable the following actions:
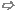
The program approximates the increase in ohmic resistance and the decrease in internal inductance over the specified frequency range, from DC up to a maximum frequency, which is specified via the parameter Model valid up to frequency (see Model valid up to frequency). The way that the impedance changes over frequency depends on the general shape of the conductor. On a PCB the typical shape type is a flat rectangle. In general, the program distinguishes between thin rectangle (strips) and circular wire shapes. For both shape types CST PCB STUDIO provides a solution for the two different kinds of model interpretation during the circuit simulation (see Circuit Simulation Aspects)
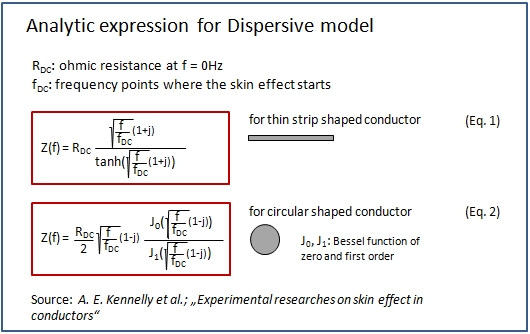
Reference:
"Experimental Researches on Skin Effect in Conductors", A.E. Kennelly; P.H. Pierce, Panama-Pacific Convention of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, San Francisco, September 16.th 1915
"Digital Signal Integrity", B. Young, Prentice Hall, 200, chapters: 7.4 and 10.3
The program approximates a constant loss angle over the specified frequency range, from DC up to a maximum frequency (see Model valid up to frequency). The crucial point in dielectric loss modeling is to keep the model causal. CST PCB STUDIO provides a solution for the two different kinds of model interpretations during the circuit simulation (see Circuit Simulation Aspects)
In case of a Dispersive model interpretation, an analytic expression is used to describe the relationship between the increase of conductance and the decrease of capacitance over the frequency range. At the frequency, specified in the material definition dialog box, the capacitance corresponds to the permittivity, also specified in the material definition dialog box.
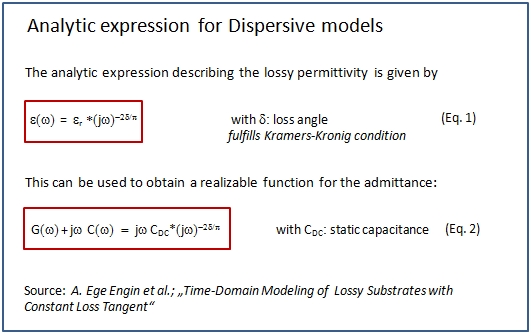
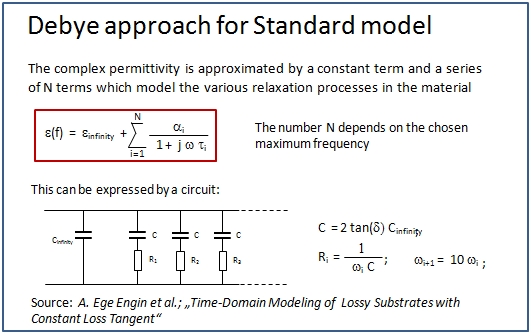
Reference:
"Time-Domain Modeling of Lossy Substrates with Constant Loss Tangent", A.E. Engin; W. Mathis; W. John; G. Sommer; H. Reichl, Signal Propagation on Interconnects, Proceedings. 8th IEEE Workshop; 9-12 May 2004, pp 151-154